mysql router
mysql router에 대하여
mysql router
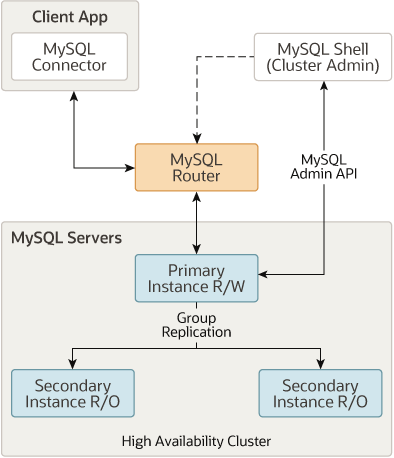
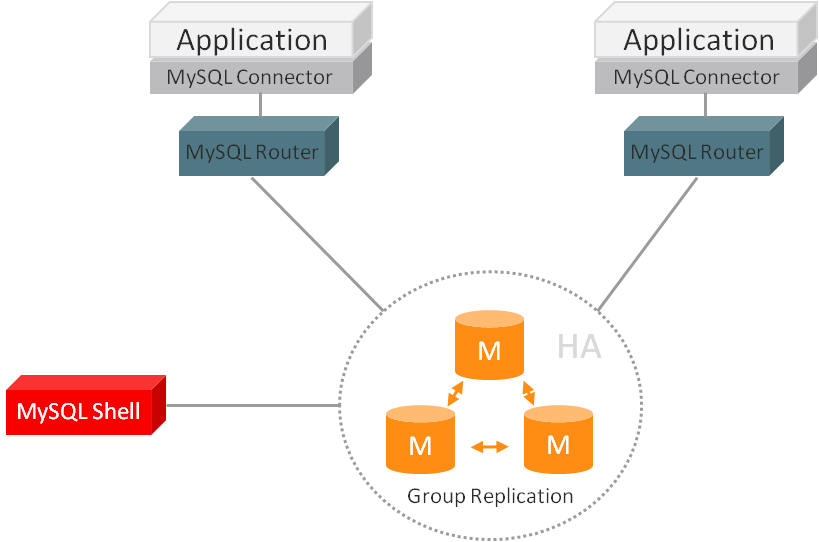
MySQL router는 InnoDB 클러스터의 구성 성분으로 애플리케이션 서버와 MySQL 서버 간의 라우팅을 제공합니다. MySQL router는 적절한 MySQL 서버로 트래픽을 라우팅하며, 고가용성과 확장성을 제공하고, 다양한 use-case에 사용될 수 있습니다.
클라이언트 애플리케이션이 failover를 처리하기 위해서는 InnoDB 클러스터의 구성에 대해서 알아야하고, 어떤 MySQL 인스턴스가 PRIMARY인지 알아야합니다. 애플리케이션이 이런 로직을 구현할 수도 있지만, MySQL router는 이런 기능을 처리하고 제공해줍니다.
MySQL은 Group Replication을 이용해서 데이터베이스를 여러 서버로 복제하고, 서버가 fail했을 때, 자동으로 failover하게 합니다. MySQL InnoDB 클러스터와 사용했을 때, MySQL Router는 프록시로서 다수의 MySQL 인스턴스를 감추고, 데이터 요청을 클러스터 인스턴스 중 하나에 매핑합니다.
cluster metadata & state
MySQL 라우터는 애플리케이션과 MySQL 서버 사이에서 동작합니다. 애플리케이션들은 일반 MySQL 서버에 연결되는 것처럼 라우터와 연결합니다. 애플리케이션이 라우터와 연결되면, 라우터는 가용한 서버 풀에서부터 적절한 MySQL 서버를 선택해서 그 서버와 애플리케이션을 연결합니다. 그 시점이후로 라우터는 애플리케이션에서 발생하는 모든 네트워크 트래픽을 해당 MySQL 서버로 포워딩합니다.
라우터는 온라인 MySQL 서버 혹은 InnoDB 클러스터의 상태, 구성 리스트를 캐쉬해놓습니다. 이 리스트는 라우터가 처음 시작할 때 설정파일의 내용으로 초기화됩니다. 이 리스트는 라우터가 --bootstrap옵션으로 bootstrap될 때 InnoDB 클러스터 서버에 의해서 생성됩니다.
캐쉬를 최신 상태로 유지하기 위해서, 메타 데이터 캐쉬 컴포넌트는 메타데이터를 가지고 있는 InnoDB 클러스터 서버와의 연결을 유지해놓습니다. 클러스터의 메타데이터는 InnoDB 클러스터가 변경될 때마다 변경됩니다. 그리고 performance_schema 테이블은 MySQL Group Replication 플러그인으로 인해 실시간으로 클러스터 상태에 맞게 변경됩니다.
라우터가 연결된 MySQL 서버의 종료를 감지하면, 새로운 MySQL 서버와 연결해서 메타데이터와 클러스터 상태를 받아오기 위해 다른 MySQL 서버와 연결을 시도합니다. 이때 애플리케이션의 MySQL 서버와의 커넥션은 끊어지고, 라우터와 재연결을 하여 온라인 MySQL 서버와 연결되야합니다.
MySQL Router Read Replica Support
MySQL 라우터는 v2_router_options.router_options.read_only_targets 메타데이터 필드에서 값을 읽어옵니다. 이 값을 통해 read-only 트래픽에 대한 라우팅 정보를 얻으려고 합니다.
v2_router_options.router_options.read_only_targets는 AdminAPI 메서드 cluster.setRoutingOption()에 의해 설정되며, 이는 read_only_targets 옵션을 사용하여 다음 값 중 하나로 라우팅 정책을 설정합니다.
all: 모든 read replica, 보조 클러스터 멤버(secondary)가 읽기 전용 트래픽에 사용됩니다.read_replicas: 읽기 복제본만 읽기 전용 트래픽에 사용됩니다.secondaries: 보조 클러스터 멤버만 읽기 전용 트래픽에 사용됩니다.
read_only_targets가 존재하지 않거나, 위 리스트에 명시되지 않는 값을 사용하면, 라우터는 기본적으로secondaries를 사용하며 경고 메세지를 기록합니다.
라우터는 클러스터 메터데이터의 소스로 read replica를 사용하지 않으며, MySQL Router 부트스트랩 명령에서 read replica를 사용할 수도 없습니다. read replica를 사용하여 부트스트랩을 시도하면 오류가 반환됩니다.
Failure Handling
MySQL 라우터는 다음과 같은 상황에서 read replica로의 라우팅을 진행하지 않습니다.
- 클러스터에 Quorum이 존재하지 않을 때,
- 모든 클러스터 멤버가 OFFLINE 상태일 때
- Group Replication 상태를 확인했을 때, 도달 가능한 멤버가 없을 때
라우티의 라우팅 정책은 다음과 같은 설정에 영향을 받습니다.
- 만약 클러스터의 상태가
INVALID이고,invalidated_cluster_policy가drop_all로 설정되면, read replicas들은 새로운 read-only 커넥션에 사용되지 않고 기존 read replica로의 커넥션도 drop됩니다. - 만약 클러스터의 상태가
INVALID이고invalidated_cluster_policy가allow_ro로 설정되면, read replicas들은 새로운 read-only 커넥션에 사용되고, 기존 커넥션들도 영향을 받지 않습니다.
connection routing
connection routing은 가용한 MySQL 서버로 MySQL 커넥션을 리다이렉트하는 것을 의미합니다. MySQL 패킷들은 검사없이 routed됩니다.
MySQL 서버로 직접 연결하지 않고 라우터로 연결한 애플리케이션은 커넥션에 실패했을 때, 재시도해서 라우터가 새로운 서버로의 연결을 제공할 수 있게 합니다. 이것은 simple redirect connection routing이라고도 알려졌는데, 애플리케이션이 커넥션을 재시도하기 때문입니다.
라우팅할 서버와 라우팅 전략은 설정 파일을 통해 정의할 수 있습니다. 다음 설정 파일의 예시는 로컬 호스트의 7002번 포트로 온 요청을 destinations에 명시된 인스턴스들로 redirect합니다. 또 routing_strategy 옵션을 사용해서 라우팅 전략을 명시할 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
[routing:simple_redirect]
bind_port = 7002
routing_strategy = round-robin
destinations = localhost:3306,localhost:3307,localhost:3308
deploying router
최적의 성능을 위해서 MySQL 라우터는 통상적으로 애플리케이션과 같은 host에 설치됩니다. 그 이유는
- TCP/IP 대신, 로컬 UNIX 도메인 소켓 커넥션을 허용하기 위해서
Unix 도메인 소켓은 라우터와 연결되는 애플리케이션에는 사용될 수 있지만, MySQL 서버와는 사용 불가합니다.
- 네트워크 지연을 줄이기 위해
- MySQL 라우터가 MySQL에 연결할 때, Router의 호스트에 대한 추가 계정이 필요 없도록 하기 위해, 예를들어
myapp@'%'같은 값 대신myapp@198.51.100.45와 같이 애플리케이션 호스트에 대해 특별히 생성된 MySQL 계정을 사용할 수 있습니다.
bootstrapping MySQL Router
다음은 MySQL Router를 InnoDB 클러스터와 함께 사용할 수 있도록 bootstrapping하는 방법을 보여주는 간단한 예입니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
$> mysqlrouter --bootstrap root@localhost:3310 --directory /tmp/myrouter
--conf-use-sockets --account routerfriend --account-create always
Please enter MySQL password for root:
# Bootstrapping MySQL Router instance at '/tmp/myrouter'...
Please enter MySQL password for routerfriend:
- Creating account(s)
- Verifying account (using it to run SQL queries that would be run by Router)
- Storing account in keyring
- Adjusting permissions of generated files
- Creating configuration /tmp/myrouter/mysqlrouter.conf
# MySQL Router configured for the InnoDB Cluster 'myCluster'
After this MySQL Router has been started with the generated configuration
$ mysqlrouter -c /tmp/myrouter/mysqlrouter.conf
the cluster 'myCluster' can be reached by connecting to:
## MySQL Classic protocol
- Read/Write Connections: localhost:6446, /tmp/myrouter/mysql.sock
- Read/Only Connections: localhost:6447, /tmp/myrouter/mysqlro.sock
## MySQL X protocol
- Read/Write Connections: localhost:6448, /tmp/myrouter/mysqlx.sock
- Read/Only Connections: localhost:6449, /tmp/myrouter/mysqlxro.sock
이 예시는 –directory 옵션을 사용하여 독립 실행형 MySQL Router 인스턴스를 생성하고, 소켓을 활성화하며, –account를 사용하여 Router의 MySQL 사용자명을 맞춤 설정하고, –account-create를 always로 설정하여 해당 계정이 존재하지 않을 때만 부트스트래핑을 수행합니다. 이 예시는 myCluster라는 InnoDB Cluster가 이미 존재한다고 가정합니다.
위 예시의 실행이 끝나면, mysqlrouter.conf파일이 생성되고, 다른 필요한 파일과 디렉터리들이 생성됩니다. 생성된 라우터 디렉터리는 다음과 같습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
$> ls -l | awk '{print $9}'
data/
log/
mysqlrouter.conf
mysqlrouter.key
run/
start.sh
stop.sh
생성된 설정 파일의 내용은 다음과 유사하게 생성됩니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
# File automatically generated during MySQL Router bootstrap
[DEFAULT]
logging_folder=/tmp/myrouter/log
runtime_folder=/tmp/myrouter/run
data_folder=/tmp/myrouter/data
keyring_path=/tmp/myrouter/data/keyring
master_key_path=/tmp/myrouter/mysqlrouter.key
connect_timeout=15
read_timeout=30
dynamic_state=/tmp/myrouter/data/state.json
[logger]
level = INFO
[metadata_cache:myCluster]
cluster_type=gr
router_id=1
user=routerfriend
metadata_cluster=myCluster
ttl=0.5
auth_cache_ttl=-1
auth_cache_refresh_interval=2
use_gr_notifications=0
[routing:myCluster_rw]
bind_address=0.0.0.0
bind_port=6446
socket=/tmp/myrouter/mysql.sock
destinations=metadata-cache://myCluster/?role=PRIMARY
routing_strategy=first-available
protocol=classic
[routing:myCluster_ro]
bind_address=0.0.0.0
bind_port=6447
socket=/tmp/myrouter/mysqlro.sock
destinations=metadata-cache://myCluster/?role=SECONDARY
routing_strategy=round-robin-with-fallback
protocol=classic
[routing:myCluster_x_rw]
bind_address=0.0.0.0
bind_port=6448
socket=/tmp/myrouter/mysqlx.sock
destinations=metadata-cache://myCluster/?role=PRIMARY
routing_strategy=first-available
protocol=x
[routing:myCluster_x_ro]
bind_address=0.0.0.0
bind_port=6449
socket=/tmp/myrouter/mysqlx.sock
destinations=metadata-cache://myCluster/?role=SECONDARY
routing_strategy=round-robin-with-fallback
protocol=x